NCERT, Class 12, Maths, Chapter 6, Misc. Ex. Solution
Q.1. Solution: NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
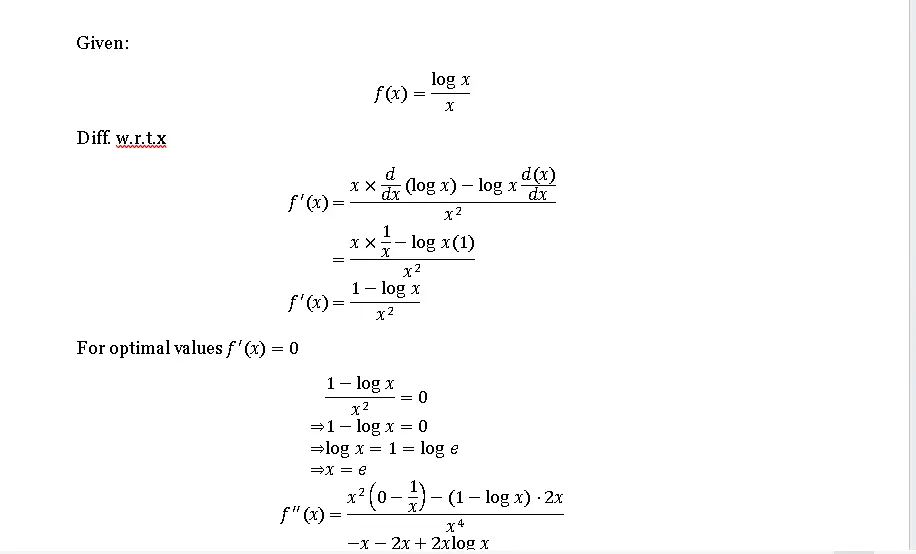
Q.1. Show that the function given by f(x) = logx/x has a maximum at x = e.
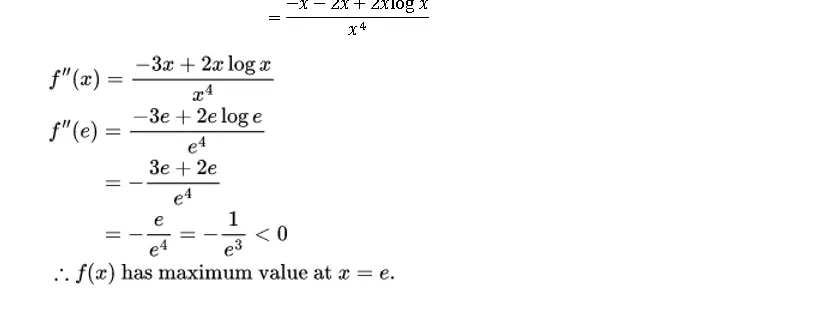

Q.2. NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
Q. 2. The two equal sides of an isosceles triangle with fixed base ‘b’ are decreasing at the rate of 3 cm per second. How fast is the area decreasing when the two equal sides are equal to the base ?
Let $A B=A C=x \mathrm{~cm}$
$$
\frac{d x}{d t}=3 \mathrm{~cm} / \mathrm{sec}
$$
To find $\frac{d A}{d t}$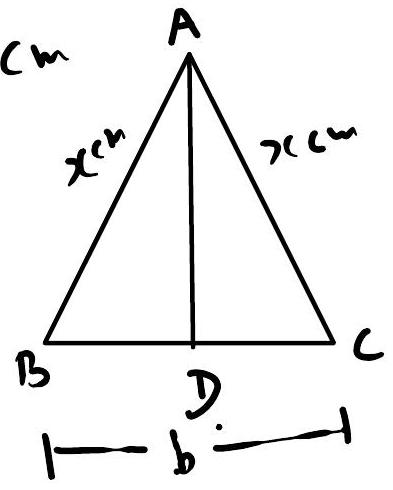
$$
\begin{aligned}
& B D=D C=\frac{b}{2} \
& A B^{2}=A D^{2}+B D^{2} \
& x^{2}=A D^{2}+\left(\frac{b}{2}\right)^{2} \
& x^{2}-\frac{b^{2}}{4}=A D^{2} \
& \Rightarrow A D=\sqrt{x^{2}-\frac{b^{2}}{4}}
\end{aligned}
$$
Area of $\triangle A B C=\frac{1}{2} \times B C \times A D$
$$
\begin{aligned}
& A=\frac{1}{2} \times b \sqrt{x^{2}-\frac{b^{2}}{4}} \
& A=\frac{1}{2} \times b \frac{\sqrt{4 x^{2}-b^{2}}}{2} \
& A=\frac{1}{4} b \sqrt{4 x^{2}-b^{2}} \
& \frac{d A}{1}=\frac{1}{4} b \cdot \frac{1}{2 \sqrt{4 x^{2}-b^{2}}} \times \frac{d x}{d t}
\end{aligned}
$$
$$
\begin{aligned}
\frac{d A}{d t} & =\frac{1}{4} b \cdot \frac{1}{2 \sqrt{4 x^{2}-b^{2}}} \cdot \frac{4 n}{d t} \
\frac{d A}{d t} & =\frac{b x}{\sqrt{4 x^{2}-b^{2}}} \cdot \frac{d n}{d t} \
\left(\frac{d A}{d t}\right)_{x=b} & =\frac{b^{2}}{\sqrt{3} b} \cdot 3 \
& =\sqrt{3} b \mathrm{~cm}^{2} / \mathrm{sec} \cdot
\end{aligned}
$$
NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
Q.3. Find the intervals in which function f given by
$$
f(x)=\frac{4 \sin x-2 x-x \cos x}{2+\cos x} \text { is }
$$
(i) increasing
(ii) decreasing.
Solution:
$$
\begin{aligned}
f(x) & =\frac{4 \sin x-x(2+\cos x)}{2+\cos x} \
f(x) & =\frac{4 \sin x}{2+\cos x}-x \
f^{\prime}(x) & =\frac{(2+\cos x) 4 \cos x-4 \sin x(0-\sin x)}{(2+\cos x)^{2}}-1 \
& =\frac{8 \cos x+4 \cos ^{2} x+4 \sin ^{2} x}{(2+\cos x)^{2}}-1 \
& =\frac{8(\cos x+4}{(2+\cos x)^{2}}-1
\end{aligned}
$$
$$
\begin{aligned}
&= \frac{8 \cos x+4-\left(4+\cos ^{2} x+4 \cos x\right)}{(2+\cos x)^{2}} \
&= \frac{8 \cos x-4 \cos x-\cos ^{2} x}{(2+\cos x)^{2}} \
&= \frac{4 \cos x-\cos ^{2} x}{(2+\cos x)^{2}} \
& f^{\prime}(x)= \frac{\cos x(4-\cos x)}{(2+\cos x)^{2}}=0 \
& \Rightarrow \cos x=0 \quad 4-\cos x=0 \
& \Rightarrow \quad x=\frac{\pi}{2} \quad \Rightarrow \quad \cos x=4
\end{aligned}
$$
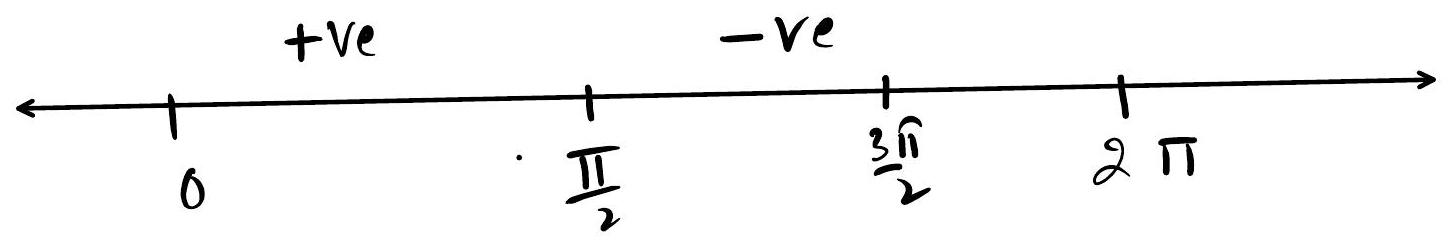
$ f(x) \text{ is increasing in } \left(0, \frac{\pi}{2}\right) \text{ and } \left(\frac{3\pi}{2}, 2\pi\right).
$
NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution. Q. 4.

Also See👉Solution for NCERT Misc. EX. Ch. 7 (INTEGRALS)
Q. 5. Find the maximum area of an isosceles triangle inscribed in the ellipse
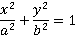
In triangle ABC:
OA = a
OD = x
BC = 2y
From the ellipse,
( \frac{x^2}{a^2} + \frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 )
Area of the triangle is:
$$
A = \frac{1}{2} \cdot BC \cdot AD
= \frac{1}{2} \cdot 2y \cdot (a+x)
$$
From the ellipse,
$$
\frac{y^2}{b^2} = 1 – \frac{x^2}{a^2}
$$
So,
$$
y = \frac{b}{a} \sqrt{a^2 – x^2}
$$
Thus the area becomes:
$$
A = \frac{b}{a} \sqrt{a^2 – x^2}\,(a+x)
$$
Differentiate:
$$
\frac{dA}{dx}
= \frac{b}{a}
\left[
\frac{-x(a+x)}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}} + \sqrt{a^2-x^2}
\right]
$$
Set derivative = 0:
$$
\frac{-x(a+x)}{\sqrt{a^2-x^2}} + \sqrt{a^2-x^2} = 0
$$
Solve:
$$
\sqrt{a^2-x^2} \left( 1 – \frac{x(a+x)}{a^2-x^2} \right)=0
$$
This gives:
$$
a^2 – x^2 = x(a+x)
$$
Simplifying:
$$
a^2 – x^2 = ax + x^2
$$
$$
a^2 = ax + 2x^2
$$
$$
2x^2 + ax – a^2 = 0
$$
Solve for x:
$$
x = \frac{-a + \sqrt{a^2 + 8a^2}}{4}
$$
$$
x = \frac{-a + 3a}{4} = \frac{a}{2}
$$
Now compute maximum area:
$$
y = \frac{b}{a} \sqrt{a^2 – \left(\frac{a}{2}\right)^2}
= \frac{b}{a} \cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}a
= \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2}\,b
$$
Finally:
$$
A_{\max} = y(a+x)
= \frac{\sqrt{3}}{2} b \left(a + \frac{a}{2}\right)
$$
$$
A_{\max} = \frac{3\sqrt{3}}{4}\,ab
$$
See Latest Posts
Free NCERT Class 12 Maths Ch 5 Misc Ex. Solution

NCERT Class 12 Maths Ch 5 Misc. Ex. Solution Q.1. NCERT Class 12 Maths Ch 5 Misc. Ex. Solution \begin{array}{l}Q.1.\ \left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)^{9}\\Solution:\ \\y=\left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)^{9}\\Differentiate\ w.r.t.\ x.\\\frac{dy}{dx} =\frac{d\left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)^{9}}{dx}\\=9\left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)^{8}\frac{d\left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)}{dx}\\=9\left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)^{8}( 6x-9)\\=9\left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)^{8} 3( 2x-3)\\=27\left( 3x^{2} -9x+5\right)( 2x-3) \ Ans.\end{array} Q.2. NCERT Class 12 Maths Ch 5 Misc.…
NCERT Class 12 Maths Miscellaneous Exercise Solutions (All Chapters)

NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter-wise Solutions Importance of NCERT Class 12 Maths Miscellaneous Exercise The NCERT Miscellaneous exercise is not just a revision exercise; this exercise is most important for students for the preparation of board exams because it includes the concept of the whole chapter, and the entire chapter’s concepts are mixed into it.…
Free NCERT Class 12 maths Chapter 2 Miscellaneous Exercise Solution

Introduction to Chapter 2: Inverse Trigonometric Functions NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter 2 Miscellaneous Exercise Solution lays the foundation of Mathematics. This chapter covers basic introduction of inverse functions of Trigonometry such as Sine, Cosine and tangent in the Trigonometry along with their properties and domain and range. Studying this is quite important for understanding…
Q. 6. NCERT class 12 maths ch 6 miscellaneous ex. solution
Q. 6. A tank with rectangular base and rectangular sides, open at the top, is to be
constructed so that its depth is 2 m and volume is 8 m³
If building of tank costs Rs 70 per sq meter for the base and Rs 45 per square meter for the sides. What is
the cost of the least expensive tank?
Solution: Volume of the tank \( =l b h \)
⇒8=lb(2) ⇒lb=4 ⇒b=\frac{4}{l}\\
\ Now, for\ the\ rectangular\ tank\ to\ be\ least\ expensive, the\ area\ of\ the\ tank\ must\ be\ minimum.\\
Area: A=Area\ of\ base+Area\ of\ 4\ walls\\
Base area: lb
Now, for the rectangular tank to be least expensive, the area of the tank must be minimum.
Area: A=Area of base+Area of 4 walls A = \text{Area of base} + \text{Area of 4 walls} A=Area of base+Area of 4 walls
Base area: lblblb
Wall area: 2h(l+b) 2h(l + b) 2h(l+b)
Thus, A=lb+2h(l+b) A = lb + 2h(l + b) A=lb+2h(l+b)
Total cost of the tank= Cost of the base + cost of 4 walls.
Cost = Area*Per unit cost
C=70×4+45×4(45)(l+4/l)
C=280 + 180(l+4/l)
\dc/dl=0+180(1-4/l^2)
\dc/dl=180(1-4/l^2)
For the least expensive tank, dc/dl=0.
1=4/l^2
l^2=4
l=2 m
\d^2c/dl^2=180×8/l^2 >0
Therefore, cost is minimum when l=4m.
Total Cost = 280+180(4)=Rs. 1000 [Put l=2 m]
Q. 7. NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
Q. 7. The sum of the perimeter of a circle and square is k, where k is some constant.
Prove that the sum of their areas is least when the side of square is double the
radius of the circle
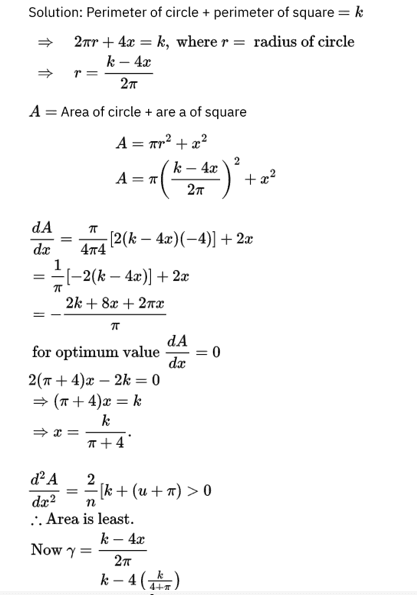
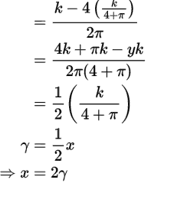
Q. 8. NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
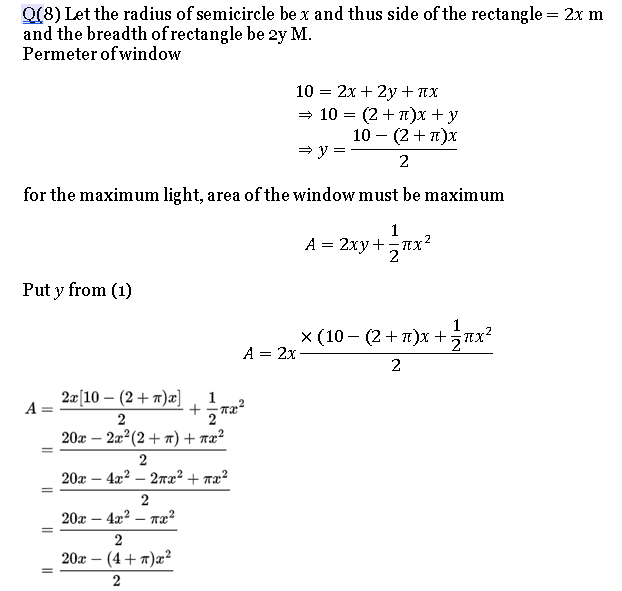
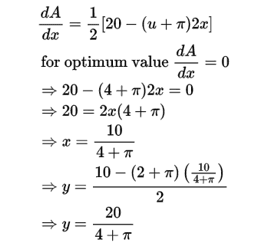
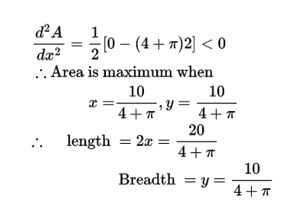
Q.9. NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
Q.9. A point on the hypotenuse of a triangle is at distance a and b from the sides of
the triangle. Show that the minimum length of the hypotenuse is
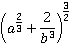
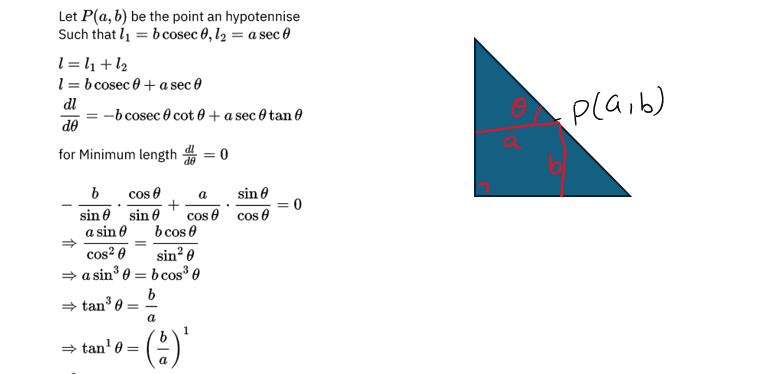
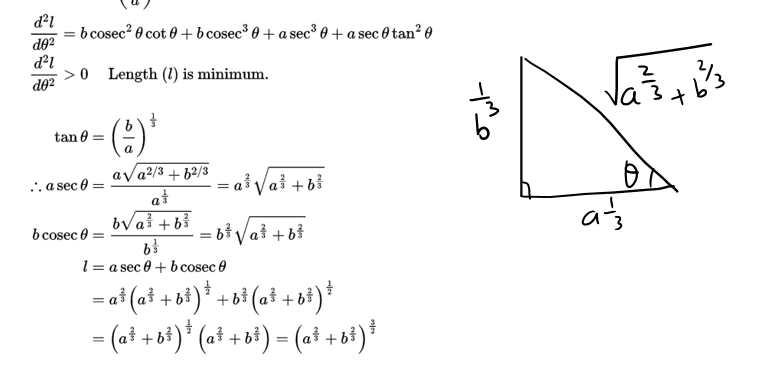

Q. 10. NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
10. Find the points at which the function f given by f (x) = (x – 2)^4(x + 1)^3
has
(i) local maxima (ii) local minima
(iii) point of inflection
soln
[
\begin{aligned}
f(x) & =(x-2)^4(x+1)^3 \\
f^{\prime}(x) & =(x-2)^4 \frac{d}{d x}(x+1)^3+(x+1)^3 \frac{d}{d x}(x-2)^4 \\
& =(x-2)^4 \cdot 3(x+1)^2+(x+1)^3 4(x-2)^3(1) \\
& =(x-2)^3(x+1)^2[3(x-2)+4(x+1)] \\
& =(x-2)^3(x+1)^2(3 x-6+4 x+4) \\
& =(x-2)^3(x+1)^2(7 x-2)
\end{aligned}
]
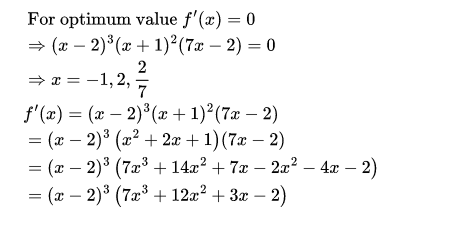
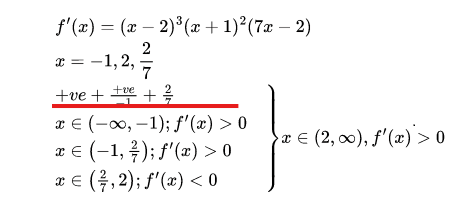
Since, the sign of f'(x) is changing from +ve to -ve at x=2/7. Hence, f(x) is maximum at x=2/7. It is changing -ve to +ve at x=2. Therefore, it is minimum at x=2. There is no change in singn at x=-1. Therefore, x=-1 is point of inflexion.
Q. 11. NCERT Maths Ch 6 Misc. Ex. solution.
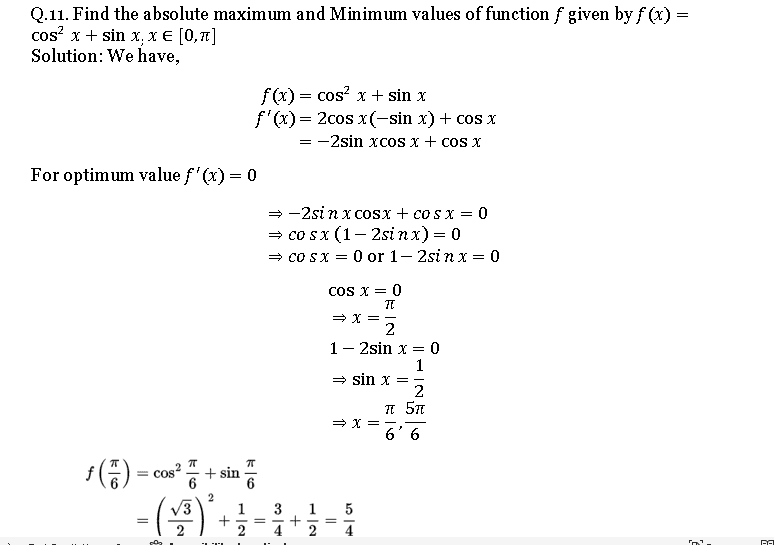
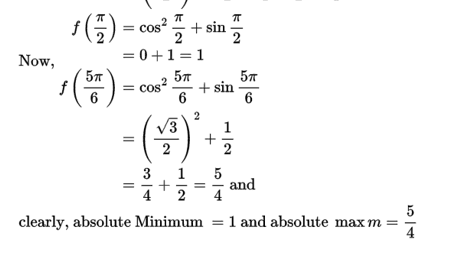
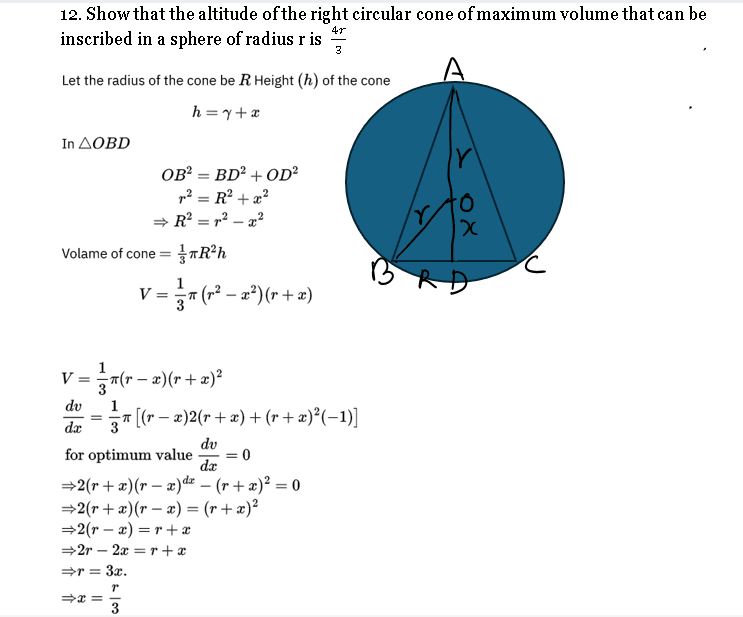
Q. 12. NCERT Solution
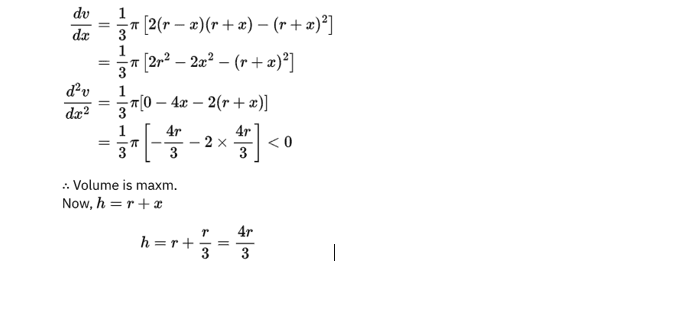
Q. 13. Solution: Ncert maths Class 12
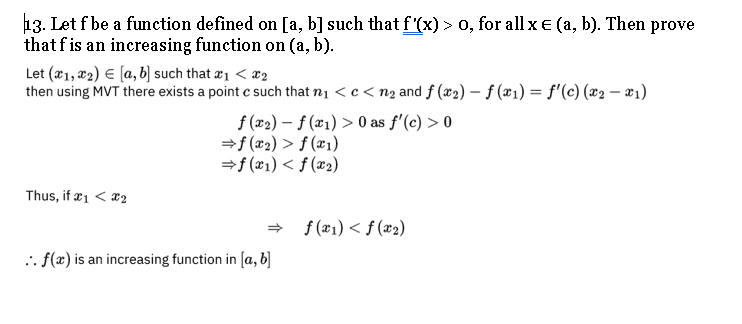
Q. 14. Solution: Ncert maths Class 12
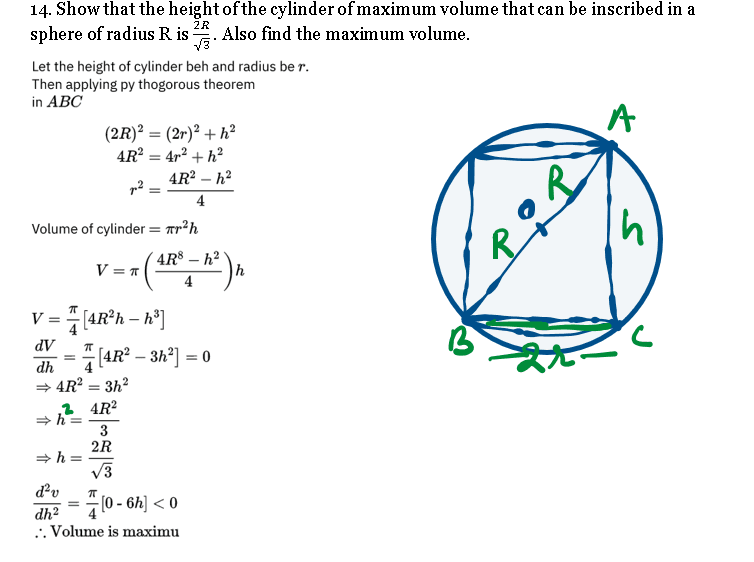
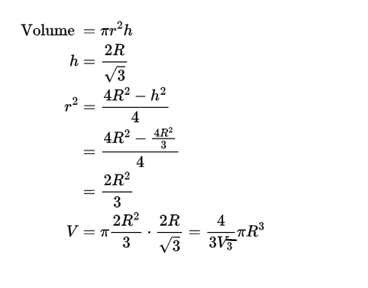
Q. 15. Solution: Ncert maths Class 12
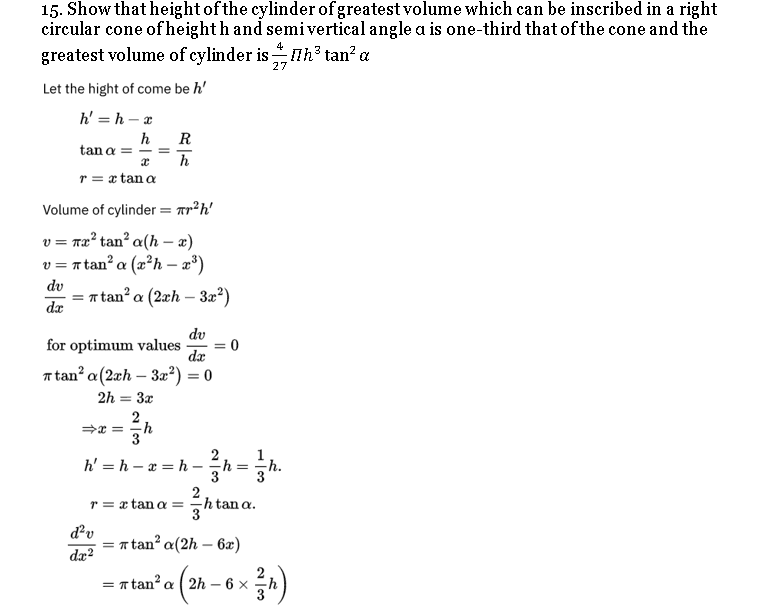
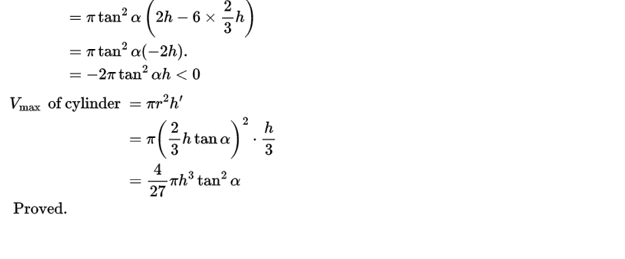
Q. 16. NCERT class 12 maths ch 6 miscellaneous ex. solution

- Free NCERT Class 12 Maths Ch 5 Misc Ex. Solution
- NCERT Class 12 Maths Miscellaneous Exercise Solutions (All Chapters)
- Free NCERT Class 12 maths Chapter 2 Miscellaneous Exercise Solution
- High School Math Online Tutoring: The Ultimate Smart Solution for Academic Success in 2025
- Free Solution to NCERT Class 12 Maths Chapter 13 (Probability)